|
|
|
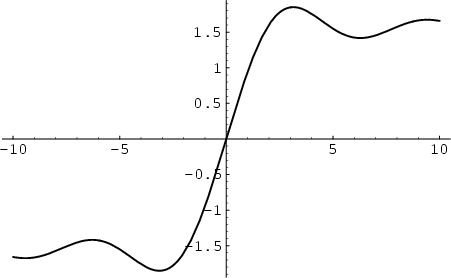
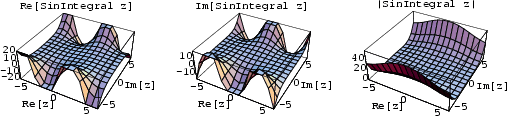
There are two types of ``sine integrals'' commonly defined,
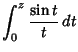 |
(1) |
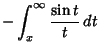 |
(2) | ||
| (3) | |||
| (4) |
| (5) |
| (6) |
To compute the integral of a sine function times a power
| (7) |
| (8) |
| (9) |
| (10) |
| (11) |
| (12) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(13) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(14) |
General integrals of the form
| (15) |
See also Chi, Cosine Integral, Exponential Integral, Nielsen's Spiral, Shi, Sici Spiral, Sinc Function
References
Abramowitz, M. and Stegun, C. A. (Eds.). ``Sine and Cosine Integrals.'' §5.2 in
Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables, 9th printing.
New York: Dover, pp. 231-233, 1972.
Arfken, G. Mathematical Methods for Physicists, 3rd ed. Orlando, FL: Academic Press, pp. 342-343, 1985.
Press, W. H.; Flannery, B. P.; Teukolsky, S. A.; and Vetterling, W. T.
``Fresnel Integrals, Cosine and Sine Integrals.'' §6.79 in
Numerical Recipes in FORTRAN: The Art of Scientific Computing, 2nd ed. Cambridge, England:
Cambridge University Press, pp. 248-252, 1992.
Spanier, J. and Oldham, K. B. ``The Cosine and Sine Integrals.''
Ch. 38 in An Atlas of Functions. Washington, DC: Hemisphere, pp. 361-372, 1987.
|
|
|
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein