|
|
|
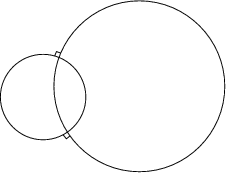
Orthogonal circles are Orthogonal Curves, i.e., they cut one another at Right Angles. Two
Circles with equations
| (1) |
| (2) |
| (3) |
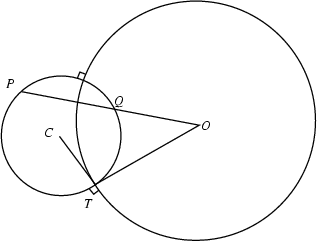
A theorem of Euclid ![]() states that, for the orthogonal circles in the above
diagram,
states that, for the orthogonal circles in the above
diagram,
| (4) |
References
Dixon, R. Mathographics. New York: Dover, pp. 65-66, 1991.
Euclid. The Thirteen Books of the Elements, 2nd ed. unabridged, Vol. 3: Books X-XIII New York: Dover, p. 36, 1956.
Pedoe, D. Circles: A Mathematical View, rev. ed. Washington, DC: Math. Assoc. Amer., p. xxiv, 1995.